Discovery Trees: Visible Tasks Tracking for ADHD developers
Posted on April 12, 2025 • 4 min read • 713 words
One of the biggest challenges of ADHD is task overwhelm—the feeling of looking at a big project and not knowing where to start. When faced with an unclear or complex task, ADHD brains often freeze up, leading to procrastination or decision paralysis.
Enter Discovery Trees.
Discovery Trees are a powerful way to break down tasks visually, make progress visible, and reduce cognitive overload. Instead of holding everything in your head, you create a branching tree of steps that shows exactly what needs to happen next. This makes it easier to stay on track, track dependencies, and avoid getting stuck.
In this post, I’ll explain how Discovery Trees work, why they’re ADHD-friendly, and how you can use them in software development.
Why ADHD Brains Struggle with Task Management
ADHD affects executive function, which makes it difficult to:
- Break down large tasks into manageable steps.
- Prioritize effectively when faced with many options.
- Remember what needs to be done next without external reminders.
Traditional to-do lists don’t always work because they are linear and overwhelming. Discovery Trees solve this by providing a visual, non-linear way to track work, making it easier to see the relationships between tasks.
How Discovery Trees Work
A Discovery Tree is a mind-map-like diagram that visually represents tasks and their dependencies.
Example: Using a Discovery Tree for a Coding Task
Let’s say we’re adding a new login feature to an app. Instead of a flat to-do list, we create a Discovery Tree:
Create a top level
Put the work to be done at the top, and list out the known work to get the top-level item done.
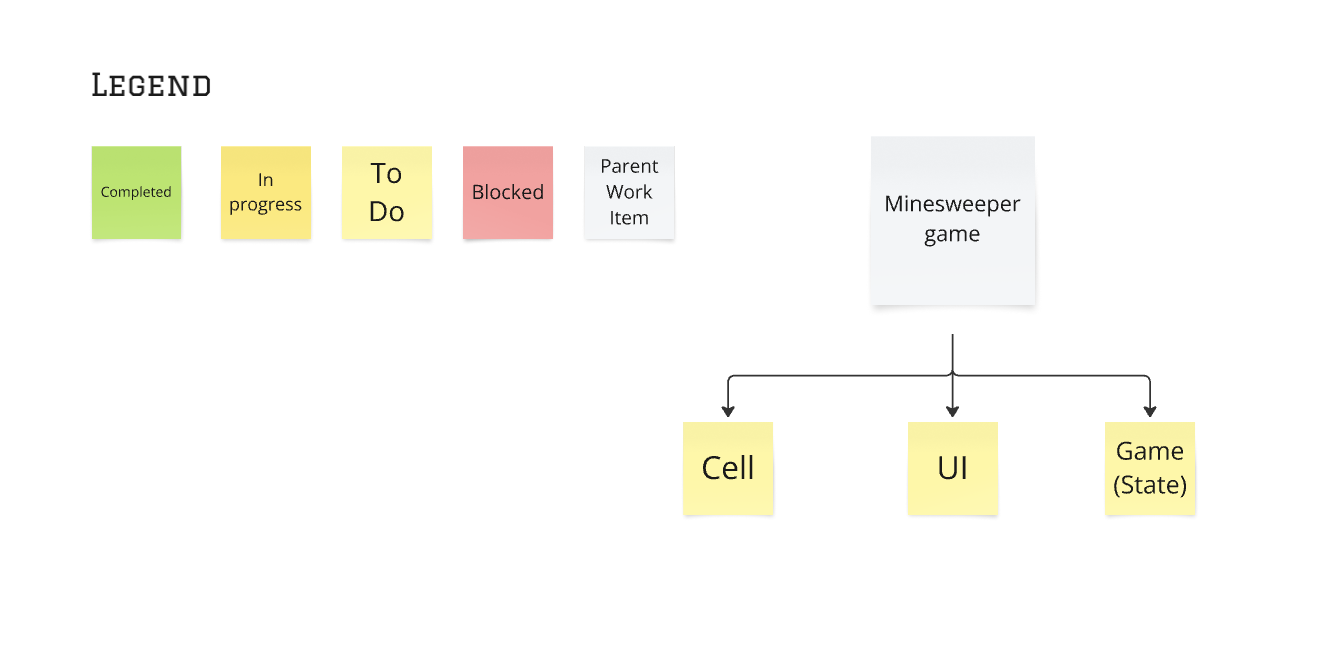
If the answer is “no”, then ask: “What is the most important part that the code doesn’t currently do?”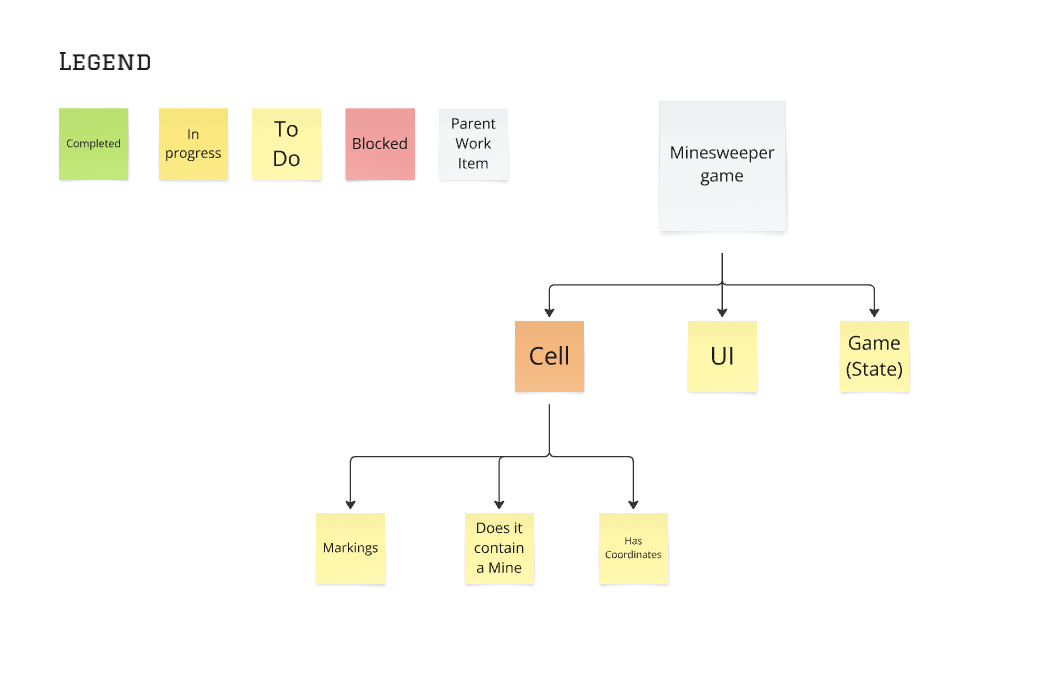
Stop and ask yourself: “Do I have an item that is small enough to start working on right now?”
If the answer is “no”, repeat the process on the branch.
Start working
If the answer is “Yes”, mark that item as “In Progress” and start working on that item.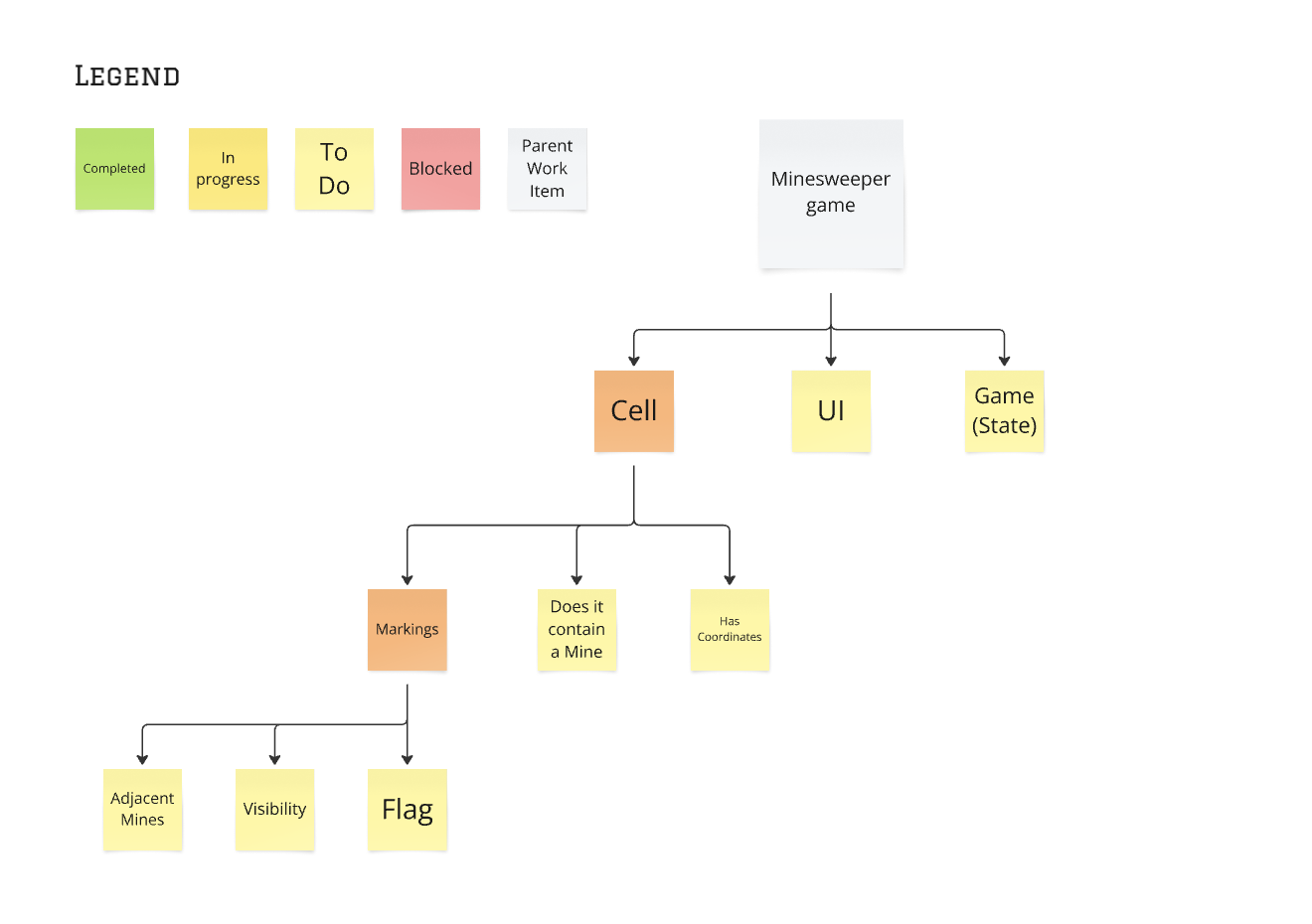
When that item is done, mark it done and move on to the next items up in the tree.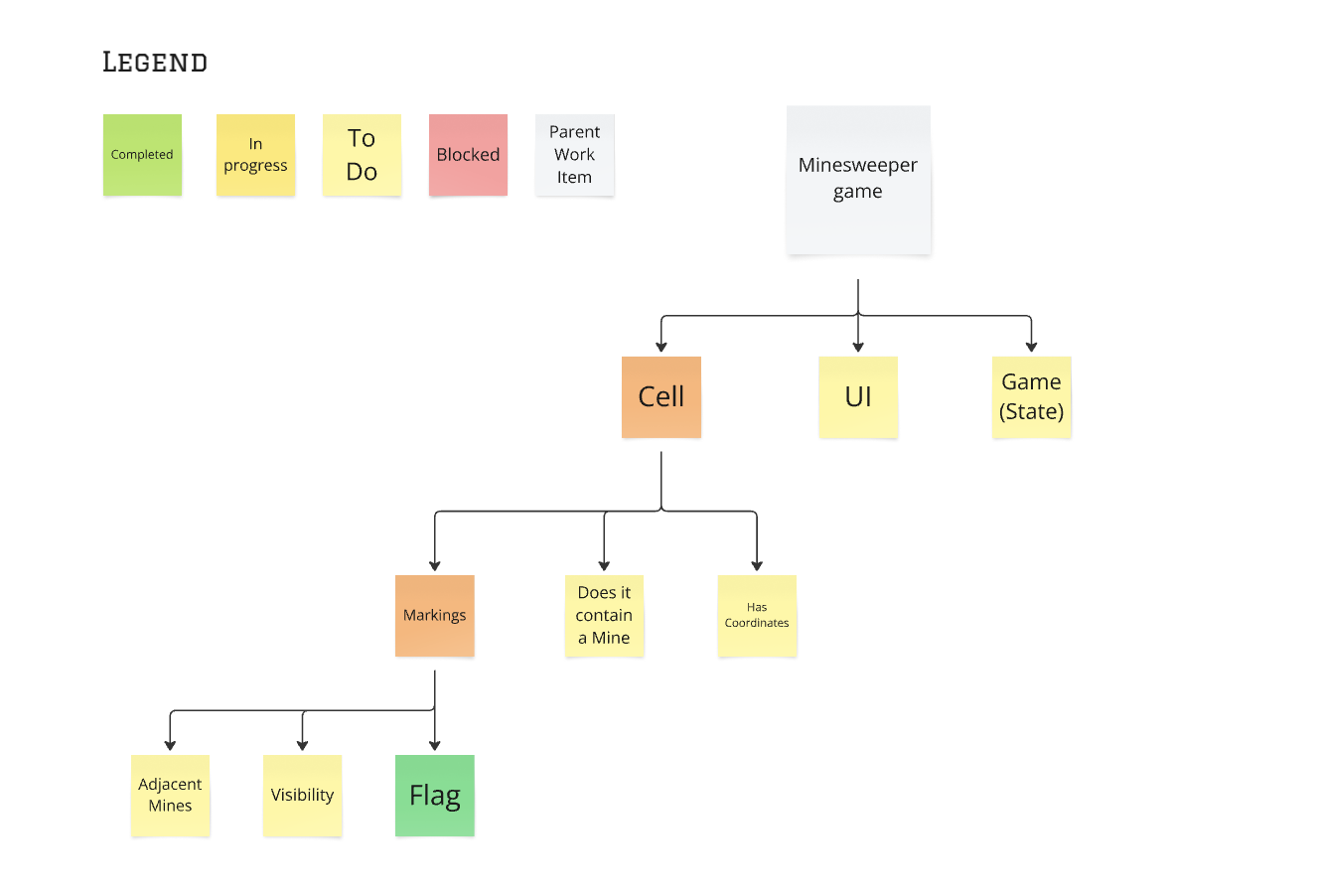
Finishing a branch
When all the branches below a leaf are done, mark that branch as done and ask yourself:
“What is the most important part that the code doesn’t currently do?”
Move onto that new branch and continue to iterate through the process.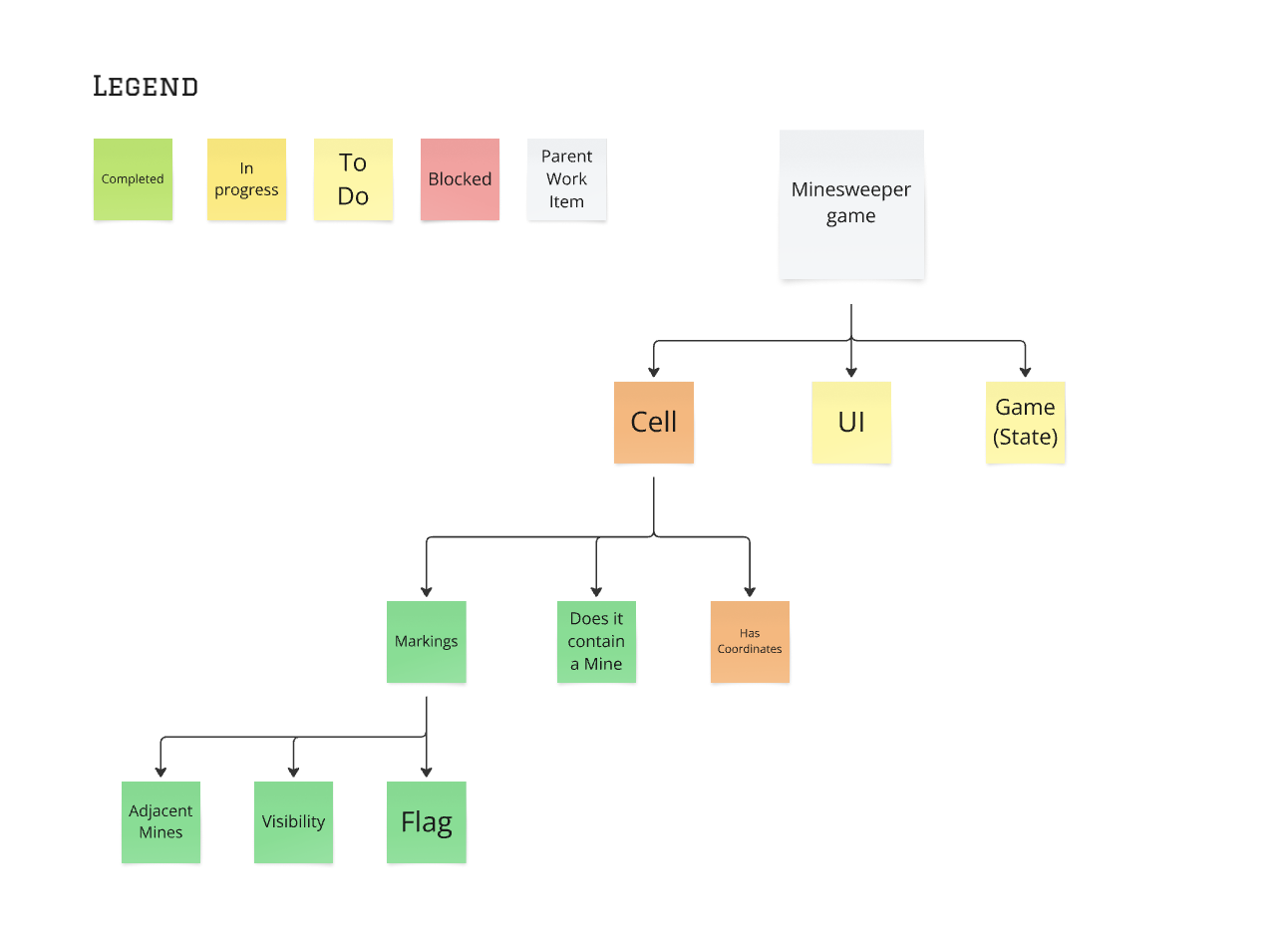
If I discover new work, I add a note to the appropriate branch and start working on that when it becomes “the most important part that the code doesn’t currently do?”
This visual approach makes it easy to see which steps are independent (can be worked on in parallel) and which tasks depend on others (must be done in order).
How Discovery Trees Help ADHD Brains
Reduces Cognitive Overload
Instead of trying to remember everything, the tree externalizes memory. You can see what needs to be done at a glance.Provides a Clear Next Step
Whenever you finish a task, you don’t have to think, “What should I do next?”, the tree shows you what’s next.Breaks Large Problems into Small, Achievable Steps
Seeing a big task as a series of tiny branches makes it feel manageable, reducing overwhelm.
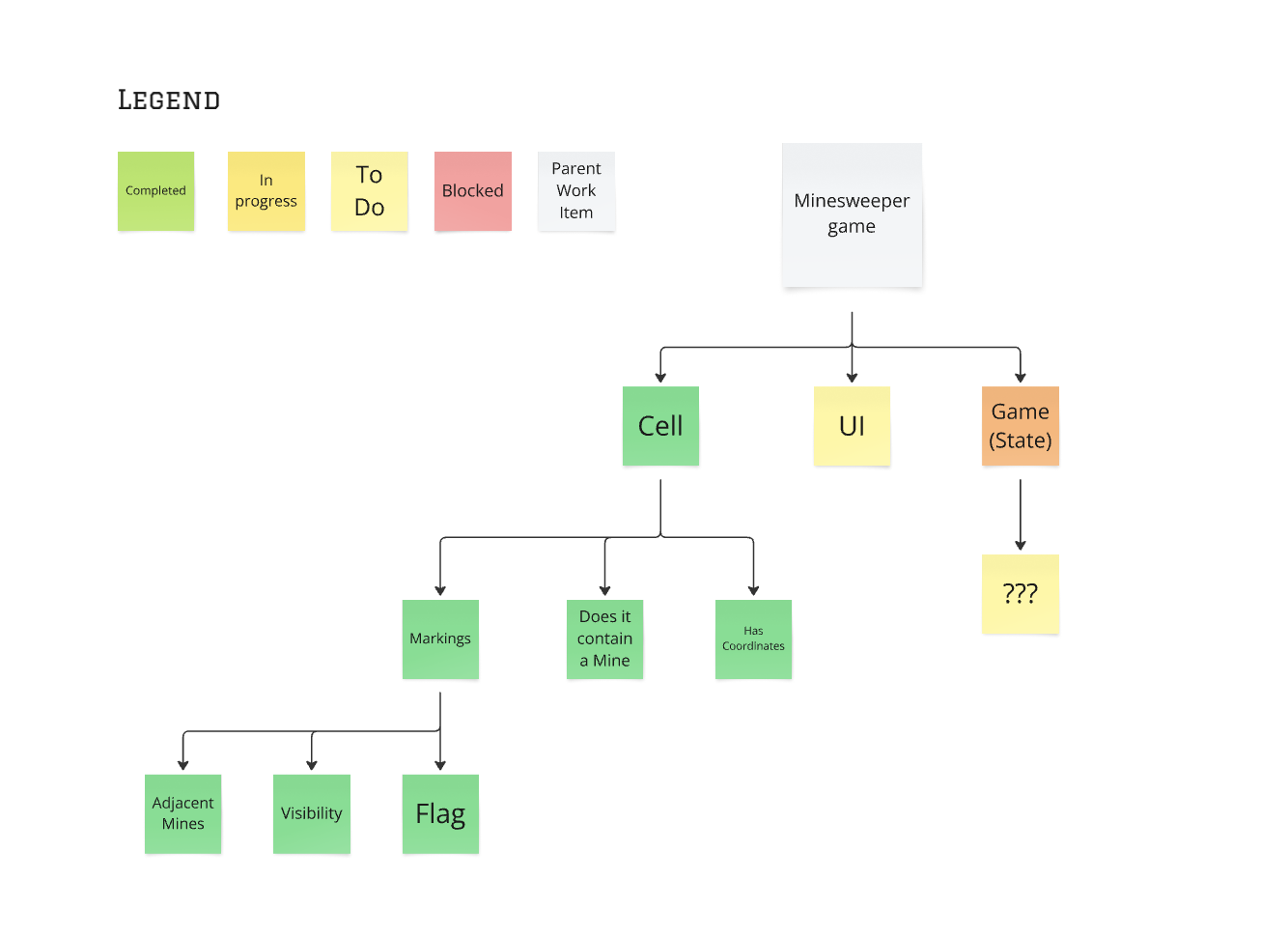
How to Create Your Own Discovery Tree
- Use whiteboards, sticky notes, or tools like Miro
- Start with the main goal at the top and break it into smaller sub-tasks
- Rearrange as needed. Discovery Trees are flexible!
Thinking Visually to Work Smarter
For ADHD developers, traditional task management tools can be frustrating, but Discovery Trees offer a dynamic, visual way to plan work and track progress.
If you’ve ever felt stuck or overwhelmed by a project, try drawing it out as a Discovery Tree. You might be surprised at how much easier it is to start, focus, and finish your work.